NATURE OF SCIENCE PROFILE OF PROSPECTIVE BIOLOGY TEACHER
Main Article Content
Abstract
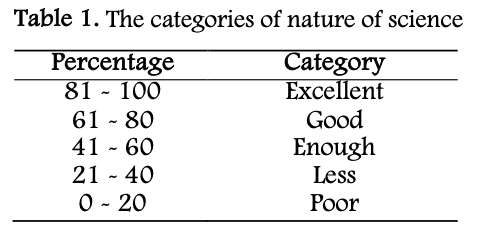
This research aims to analyze the understanding of prospective biology teachers regarding the Nature of Science (NOS) as an important foundation in science education. The method used is a quantitative descriptive survey with the Views of Nature of Science (VNOS) Form B questionnaire instrument. This research involves first-year students of the biology education program as participants. Data analysis was conducted using descriptive statistics to determine the percentage of their understanding of NOS based on seven indicator aspects, namely the provisional nature, empirical basis, subjectivity, human inference, creativity, socio-cultural context, and the distinction between observation and inference. The results show that the average understanding of NOS among students falls into the good category with a score of 76%. However, understanding of the aspects of subjectivity, socio-cultural context, and the difference between scientific theory and scientific law still needs to be improved. A strong understanding of NOS will support prospective teachers in teaching science more critically and meaningfully to students, as well as prepare them to face scientific challenges in the future.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
References
Adi, Y. K., & Widodo, A. (2018). Pemahaman Hakikat Sains Pada Guru Dan Siswa Sekolah Dasar. Edukasi Journal, 10(1), 55–72. https://doi.org/10.31603/edukasi.v10i1.1831
Aflalo, E. (2014). Advancing the perceptions of the nature of science (NOS): integrating teaching the NOS in a science content course. Research in Science and Technological Education, 32(3), 298–317. https://doi.org/10.1080/02635143.2014.944492
Arslan, O., & Sagir, U. (2020). Representation of Nature of Science in Matter and Its Nature Subject Area of Science Textbooks. International Online Journal of Educational Sciences, 12(5), 124–143. https://doi.org/10.15345/iojes.2020.05.010
Astuti, T. P. (2019). Model Problem Based Learning dengan Mind Mapping dalam Pembelajaran IPA Abad 21. Proceeding of Biology Education, 3(1), 64–73. https://doi.org/10.21009/pbe.3-1.9
Cullinane, A., & Erduran, S. (2022). Investigating Pre-Service Teachers’ Understanding of Nature of Science: Contributions of An Assessment Tool Based on the Reconceptualized Family Resemblance Approach. Interdisciplinary Journal of Environmental and Science Education, 18(4), e2290. https://doi.org/10.21601/ijese/12111
Curtis, A. (2015). The science of subjectivity. Geology, 40(1), 95–96. https://doi.org/10.1130/focus012012.1
Donohue, K., Buck, G. A., & Akerson, V. (2020). Where’s the science? Exploring a new science teacher educator’s theoretical and practical understandings of scientific inquiry. International Journal of Research in Education and Science, 6(1), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.46328/ijres.v6i1.571
Hardianty, N. (2015). Nature of Science : Bagian Penting Dari Literasi Sains. Prosiding Simposium Nasional Inovasi Dan Pembelajaran Sains 2015 (SNIPS 2015), 2015(Snips), 441–444.
Kaya, S., Erduran, S., Birdthistle, N., & McCormack, O. (2018). Looking at the Social Aspects of Nature of Science in Science Education Through a New Lens. Science & Education, 27(5–6), 457–478. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11191-018-9990-y
Khishfe, R. (2017). Consistency of nature of science views across scientific and socio-scientific contexts. International Journal of Science Education, 39(4), 403–432. https://doi.org/10.1080/09500693.2017.1287976
Kind, P., & Osborne, J. (2017). Styles of Scientific Reasoning: A Cultural Rationale for Science Education? Science Education, 101(1), 8–31. https://doi.org/10.1002/sce.21251
Kolb, D. A., & Kolb, A. Y. (2017). The Experiential Educator: Principles and Practices of Experiential Learning How You Learn Is How You Live View project Learning Sustainability View project. April, 565. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/316342276_The_Experiential_Educator_Principles_and_Practices_of_Experiential_Learning%0Ahttps://www.researchgate.net/publication/316342276
Muslih, M. (2020). Sains, dari Pengetahuan Khusus, Aktivitas Ilmiah, hingga Disiplin Ilmu. Falsafah Sains, July 2019, 27–53.
Muttaqin, J., Sarjan, M. Z., Rokhmat, M., Muliadi, J., Azizi, A., Ardiansyah, A., Hamidi, B., Pauzi, H., Yamin, I., Rasyidi, M., Rahmatiah, M.,
Sudirman, R., & Khery, S. (2022). Pemahaman Nature of Science (Hakekat IPA) Bagi Guru IPA: Solusi Membelajarkan IPA Multidimensi. Jurnal Ilmiah Wahana Pendidikan, 8(21), 8.
Prachagool, V., & Nuangchalerm, P. (2019). Investigating understanding the nature of science. International Journal of Evaluation and Research in Education, 8(4), 719–725. https://doi.org/10.11591/ijere.v8i4.20282
Sukaesih, S., Zubaidah, S., Mahanal, S., & Listyorini, D. (2022). Enhancing students’ nature of science understanding through project-based learning and mind mapping. International Journal of Evaluation and Research in Education, 11(4), 1704–1713. https://doi.org/10.11591/ijere.v11i4.22282
Widowati, A., Atun, S., Suryadarma, I. G. P., Wiyarsi, A., & Yani, L. A. F. (2018). The profile of students’ views of nature of science (NOS) in Junior High School of Yogyakarta city. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2014(March 2018). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5054496